World Tuberculosis Day
Health Education
WHAT IS TUBERCULOSIS?
“Tuberculosis” is defined as an infectious disease caused by a bacterium; that most commonly affects the lungs. It can also be a crippling and deadly disease, and is on the rise in both developed and developing worlds. Globally, it is the leading cause of deaths resulting from a single infectious disease. Currently, it kills “three million people” a year and could claim up to 30 million lives if not controlled.[1]
[1] 08 Feb 2001. A brief history of Tuberculosis. NMJS National Tuberculosis Center. 12 Oct 2004 <http://www.umdnj.edu/ntbcweb/history.html>
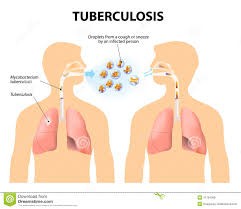
HOW IS TB SPREAD?
TB (Tuberculosis) is spread from person to person through the air. When people with lung TB cough, sneeze or spit, they propel the TB germs into the air. A person needs to inhale only a few of these germs to be infected.
About one-third of the world’s population has latent TB, which means people have been infected by TB Bacteria but are not (yet) ill with the disease and cannot transmit the disease.
People infected with the TB bacteria have a 10% lifetime risk of falling ill with TB. However, persons with compromised immune systems, such as people living with HIV, malnutrition or diabetes, or people who use tobacco, have a much higher risk of falling ill.
When a person develops active TB disease, the symptoms (such as cough, fever, night sweats, or weight loss) may be mild for many months. This can lead to delays in seeking care, and results in transmission of the bacteria to others. People with active TB can infect 10-15 other people through close contact over the course of a year. Without proper treatment, 45% of HIV –negative people with TB on average and nearly all HIV-positive people will die.
SYMPTOMS OF TUBERCULOSIS
While latent TB is symptomless, the symptoms of active TB including the following:
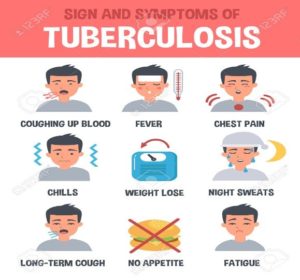
- Coughing, sometimes with mucus or blood
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of weight
- Loss of appetite
- Night sweats
GET TESTED:

- When someone comes into contact with tuberculosis or feels as if they become infected by tuberculosis, they should call a doctor and order a skin test.
- The doctor will inject a small amount of tuberculin under the skin.
- If a person has been exposed to tuberculosis a swelling will develop around the spot where the skin test is given. [1]
